locust_3 目标:使用locust 对websocket接口做压测
大佬文档:https://www.cnblogs.com/shenh/p/18321028
需要的库: 1 2 3 pip install websockets locust websocket-client # 更新最新版本locust pip install --upgrade locust
服务端demo 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 import asyncioimport websocketsimport jsonasync def handle_connection (websocket, path ): print (f"New connection from {path} " ) try : async for message in websocket: print (f"Received: {message} " ) response = f"Echo: {message} " response_data = { "data" : ["Example" , "Data" , "For" , "hello_world" ] } await websocket.send(json.dumps(response_data)) except websockets.ConnectionClosed as e: print (f"Connection closed: {e} " ) async def main (): server = await websockets.serve(handle_connection, "localhost" , 8765 ) print ("WebSocket server started on ws://localhost:8765" ) await server.wait_closed() if __name__ == "__main__" : asyncio.run(main())
客户端demo 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 from locust import task, between, User, eventsimport os, json, time, websocket, socket, sysclass WebSocketClient (object ): def __init__ (self, host ): self.host = host self.ws = websocket.WebSocket() def connect (self, url ): self.ws.connect(url=self.host + url) return self.ws def send (self, msg ): self.ws.send(msg) def recv (self ): return self.ws.recv() def close (self ): self.ws.close() class WebsocketLocust (User ): abstract = True def __init__ (self, *args, **kwargs ): super (WebsocketLocust, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs) self.client = WebSocketClient('ws://localhost:8765' ) class UserTask (WebsocketLocust ): def on_start (self ): '''初始化数据,每个虚拟用户只执行一次''' self.url = "/" self.ws = self.client.connect(self.url) self.params = {'name' :'hello world' } @task def test (self ): start_time = time.time() try : self.ws.send(json.dumps(self.params)) r = self.ws.recv() total_time = time.time() - start_time result = json.loads(r)['data' ] print (result) print (type (result)) assert result[0 ] == 'Example' events.request.fire(request_type="websockt" , name=self.url, response_time=total_time * 1000 , response_length=len (r), response=result) except AssertionError: events.request.fire(request_type="websockt" , name=self.url, response_time=total_time * 1000 , response_length=0 , exception=f"断言错误,response:{result} " ) except socket.timeout: events.user_error.fire(user_instance=UserTask, exception='Timeout' , tb=sys.exc_info()[2 ]) except Exception as e: events.user_error.fire(user_instance=UserTask, exception=e, tb=sys.exc_info()[2 ]) def on_stop (self ): '''销毁数据,每个虚拟用户只执行一次''' self.ws.close() if __name__ == "__main__" : os.system('locust -f locust_test.py' )
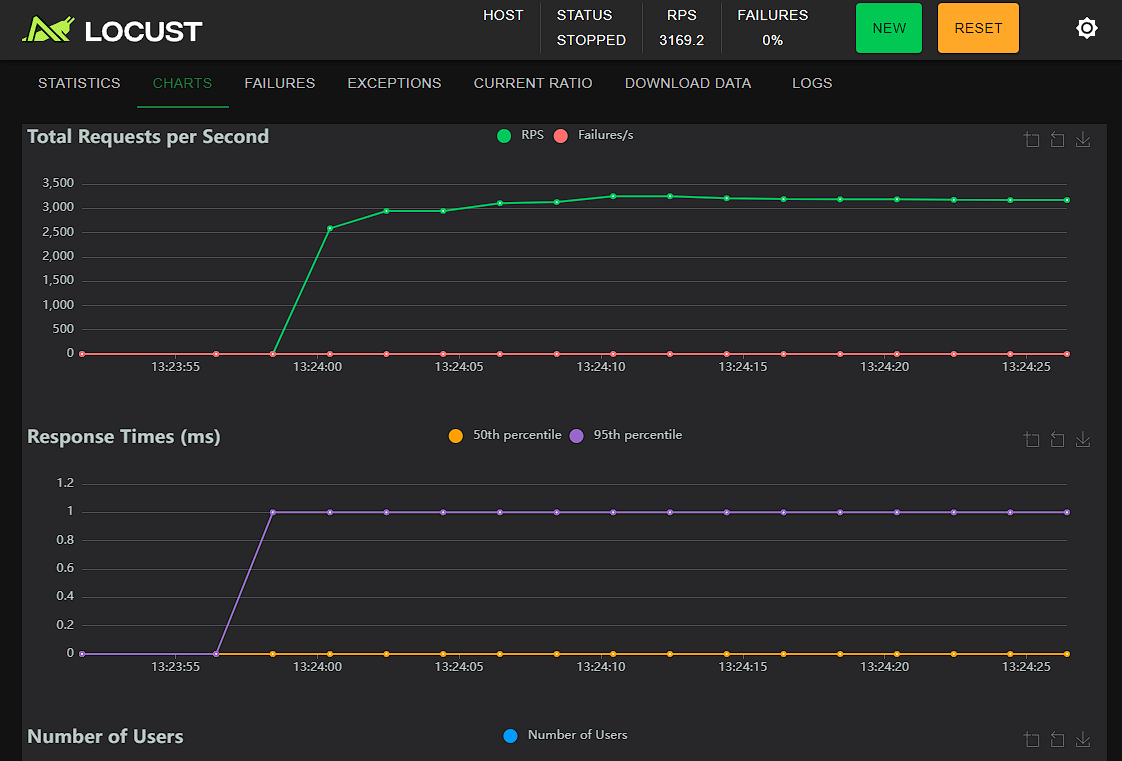
效果: